क्या हीट वेव जलवायु परिवर्तन का मुख्य कारण है?
हाल के महीनों में, चरम मौसम की घटनाओं की एक श्रृंखला ने वैश्विक ध्यान आकर्षित किया है, जो हीटवेव और जलवायु परिवर्तन के तत्काल और परस्पर जुड़े मुद्दों को उजागर करती है। जुलाई 2024 में, फ्रांस और अन्य भूमध्यसागरीय देशों में एक महत्वपूर्ण हीटवेव आई, जिसके परिणामस्वरूप खतरनाक परिणाम सामने आए। वर्ल्ड वेदर एट्रिब्यूशन (WWA) के एक विश्लेषण के अनुसार, यह हीटवेव मानव-प्रेरित जलवायु परिवर्तन के बिना “लगभग असंभव” होती। यह एक महत्वपूर्ण प्रश्न उठाता है: क्या हीटवेव जलवायु परिवर्तन का मुख्य कारण है, या यह एक बड़ी समस्या का लक्षण है? हीटवेव और जलवायु परिवर्तन को समझना हीटवेव अत्यधिक गर्म मौसम की एक विस्तारित अवधि है, जो स्वास्थ्य और बुनियादी ढांचे के लिए खतरनाक हो सकती है। जबकि हीटवेव पूरे इतिहास में हुई हैं, ग्लोबल वार्मिंग के कारण उनकी आवृत्ति और तीव्रता में वृद्धि हुई है। मानवीय गतिविधियों, विशेष रूप से जीवाश्म ईंधन के जलने से वायुमंडल में ग्रीनहाउस गैसों की सांद्रता बढ़ गई है। ये गैसें गर्मी को फँसाती हैं, जिससे पृथ्वी का तापमान बढ़ता है – एक घटना जिसे ग्लोबल वार्मिंग के रूप में जाना जाता है।
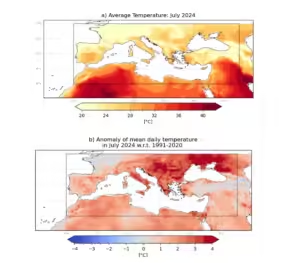
जुलाई 2024 की हीटवेव, जिसने फ्रांस और भूमध्य सागर को प्रभावित किया, इसका एक स्पष्ट उदाहरण है। 2024 के पेरिस ओलंपिक में खिलाड़ियों को अत्यधिक गर्मी से निपटने के लिए अतिरिक्त ब्रेक दिए गए थे। WWA के विश्लेषण से पता चलता है कि मानव-कारण वार्मिंग के कारण ऐसी हीटवेव अब अपेक्षाकृत आम हो गई हैं और लगभग एक दशक में एक बार होने की उम्मीद है। मानव-प्रेरित जलवायु परिवर्तन के बिना, पेरिस हीटवेव के दौरान लगभग 3°C ठंडा होता, जिससे यह बाहरी गतिविधियों के लिए सुरक्षित होता।
जुलाई 2024 की भूमध्यसागरीय हीटवेव जुलाई 2024 की भूमध्यसागरीय हीटवेव ने ग्रीस, इटली, स्पेन और मोरक्को सहित कई देशों को प्रभावित किया। मोरक्को में तापमान 48°C तक पहुँच गया, जिससे कम से कम 21 लोगों की मौत हो गई। ग्रीस और उत्तरी मैसेडोनिया में जंगल में आग लगने की खबरें आईं, जो अत्यधिक गर्मी के विनाशकारी प्रभावों को और स्पष्ट करती हैं। हीटवेव एक “हीट डोम” द्वारा संचालित थी, जो एक बड़े पैमाने पर उच्च दबाव वाला क्षेत्र है जो सतह के पास गर्म हवा को फँसाता है। यह हीट डोम जुलाई की शुरुआत में विकसित हुआ और अगले हफ़्तों में मध्य और पूर्वी यूरोप में फैल गया। WWA के अनुसार, इस तरह की गर्मी के अनुकूल न होने वाले शीर्ष ओलंपिक एथलीटों के प्रदर्शन में गिरावट और गर्मी से संबंधित बीमारियों में वृद्धि का अनुभव हो सकता है।
बड़ी तस्वीर: जलवायु परिवर्तन
जबकि जुलाई 2024 जैसी हीटवेव वास्तव में खतरनाक हैं, वे जलवायु परिवर्तन का मूल कारण नहीं हैं, बल्कि एक लक्षण हैं। जलवायु परिवर्तन का प्राथमिक कारण मानवीय गतिविधियों के कारण ग्रीनहाउस गैसों में वृद्धि है। इसमें जीवाश्म ईंधन जलाने, वनों की कटाई और औद्योगिक प्रक्रियाओं से कार्बन डाइऑक्साइड उत्सर्जन शामिल है।
WWA के विश्लेषण से पता चलता है कि आज की जलवायु में हीटवेव पूर्व-औद्योगिक दुनिया की तुलना में 1.7-3.5 डिग्री सेल्सियस अधिक गर्म हैं। यह जलवायु पर एक महत्वपूर्ण मानवीय प्रभाव को इंगित करता है। जैसे-जैसे वैश्विक तापमान बढ़ता जा रहा है, हीटवेव, तूफान और भारी वर्षा जैसी चरम मौसम की घटनाएँ अधिक लगातार और गंभीर होती जा रही हैं।
आगे का रास्ता
जलवायु परिवर्तन को संबोधित करने के लिए एक बहुआयामी दृष्टिकोण की आवश्यकता है। ग्रीनहाउस गैस उत्सर्जन को कम करना महत्वपूर्ण है। इसे अक्षय ऊर्जा स्रोतों में बदलाव, ऊर्जा दक्षता में सुधार और कृषि और उद्योग में संधारणीय प्रथाओं को अपनाकर हासिल किया जा सकता है। इसके अतिरिक्त, चरम मौसम की घटनाओं का सामना करने के लिए बुनियादी ढांचे और नीतियों को विकसित करके जलवायु लचीलापन बढ़ाना आवश्यक है।
सार्वजनिक जागरूकता और अंतर्राष्ट्रीय सहयोग भी महत्वपूर्ण है। हाल ही में हुई हीटवेव और अन्य चरम मौसम की घटनाओं को सरकारों, व्यवसायों और व्यक्तियों के लिए जलवायु परिवर्तन के खिलाफ सार्थक कार्रवाई करने के लिए एक चेतावनी के रूप में काम करना चाहिए।
हीटवेव जलवायु परिवर्तन का एक महत्वपूर्ण और खतरनाक लक्षण है, लेकिन वे इसका मुख्य कारण नहीं हैं। अंतर्निहित मुद्दा मानवीय गतिविधियों के कारण ग्रीनहाउस गैसों में वृद्धि है। जलवायु परिवर्तन को संबोधित करने के लिए उत्सर्जन को कम करने और लचीलापन बढ़ाने के लिए तत्काल और निरंतर प्रयासों की आवश्यकता है। जलवायु परिवर्तन के कारणों को समझकर और उन पर कार्रवाई करके, हम चरम मौसम की घटनाओं के प्रभावों को कम कर सकते हैं और भविष्य की पीढ़ियों के लिए अपने ग्रह की रक्षा कर सकते हैं।
IN ENGLISH,
Is Heat Wave Main Cause of Climate Change?
In recent months, a series of extreme weather events have captured global attention, highlighting the urgent and interconnected issues of heatwaves and climate change. In July 2024, a significant heatwave swept through France and other Mediterranean countries, leading to alarming consequences. According to an analysis by World Weather Attribution (WWA), this heatwave would have been “virtually impossible” without human-induced climate change. This raises a crucial question: Is the heat wave the main cause of climate change, or is it a symptom of a larger problem?
Understanding Heatwaves and Climate Change
A heatwave is an extended period of excessively hot weather, which can be dangerous to health and infrastructure. While heatwaves have occurred throughout history, their frequency and intensity have increased due to global warming. Human activities, particularly the burning of fossil fuels, have led to higher concentrations of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. These gases trap heat, causing the Earth’s temperature to rise—a phenomenon known as global warming.
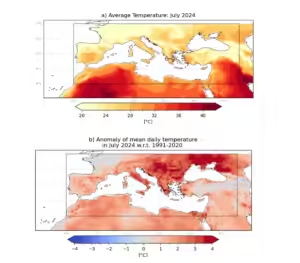
The July 2024 heatwave, which struck France and the Mediterranean, serves as a stark example. Players at the 2024 Paris Olympics were given extra breaks to cope with the extreme heat. The WWA’s analysis suggests that such heatwaves are now relatively common due to human-caused warming and are expected to occur about once a decade. Without human-induced climate change, Paris would have been about 3°C cooler during the heatwave, making it safer for outdoor activities.
The Mediterranean Heatwave of July 2024
The Mediterranean heatwave of July 2024 impacted several countries, including Greece, Italy, Spain, and Morocco. Temperatures reached as high as 48°C in Morocco, causing at least 21 deaths. Wildfires were reported in Greece and North Macedonia, further illustrating the devastating effects of extreme heat.
The heatwave was driven by a “heat dome,” a large-scale high-pressure area that traps warm air near the surface. This heat dome developed in early July and expanded into central and eastern Europe in the following weeks. According to WWA, elite Olympic athletes not acclimated to such heat might experience a decline in performance and an increase in heat-related illnesses.
The Bigger Picture: Climate Change
While heatwaves like the one in July 2024 are indeed alarming, they are not the root cause of climate change but rather a symptom. The primary cause of climate change is the increase in greenhouse gases due to human activities. This includes carbon dioxide emissions from burning fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial processes.
The WWA’s analysis shows that heatwaves in today’s climate are 1.7-3.5°C hotter than in the pre-industrial world. This indicates a significant human impact on the climate. As global temperatures continue to rise, extreme weather events like heatwaves, storms, and heavy rainfall are becoming more frequent and severe.
The Way Forward
Addressing climate change requires a multifaceted approach. Reducing greenhouse gas emissions is crucial. This can be achieved through transitioning to renewable energy sources, improving energy efficiency, and adopting sustainable practices in agriculture and industry. Additionally, enhancing climate resilience by developing infrastructure and policies to withstand extreme weather events is essential.
Public awareness and international cooperation are also vital. The recent heatwave and other extreme weather events should serve as a wake-up call for governments, businesses, and individuals to take meaningful action against climate change.
Heatwaves are a significant and dangerous symptom of climate change, but they are not the main cause. The underlying issue is the rise in greenhouse gases due to human activities. Addressing climate change requires immediate and sustained efforts to reduce emissions and enhance resilience. By understanding and acting on the causes of climate change, we can mitigate the impacts of extreme weather events and protect our planet for future generations.